Performing a BFS on all directions in a Binary Tree
I've tried this problem before pre-pandemic and failed to realize that it requires something not very common: to perform a BFS on a binary tree across all directions. The "across all directions" means that it is necessary to create the link node -> parent. This can be done using a simple DFS storing the info in a hash table. Then once you find the node related to K (another DFS), then perform a BFS going left, right, parent. All the code together should run in linear time, with a constant 3 (O(3N)). Code is below, cheers, ACC.
Closest Leaf in a Binary Tree - LeetCode
Given the root of a binary tree where every node has a unique value and a target integer k, return the value of the nearest leaf node to the target k in the tree.
Nearest to a leaf means the least number of edges traveled on the binary tree to reach any leaf of the tree. Also, a node is called a leaf if it has no children.
Example 1:
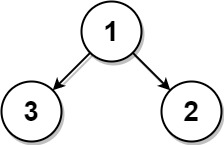
Input: root = [1,3,2], k = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: Either 2 or 3 is the nearest leaf node to the target of 1.
Example 2:

Input: root = [1], k = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: The nearest leaf node is the root node itself.
Example 3:
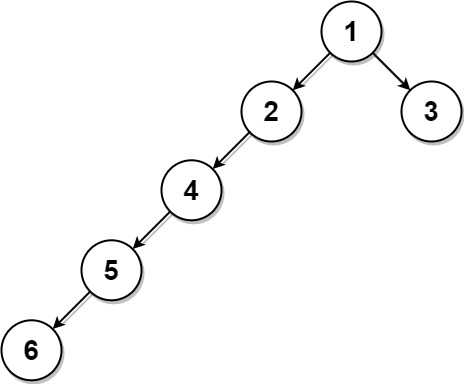
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5,null,6], k = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: The leaf node with value 3 (and not the leaf node with value 6) is nearest to the node with value 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1000- All the values of the tree are unique.
- There exist some node in the tree where
Node.val == k.
public class QueueItem
{
public TreeNode node = null;
public int steps = 0;
public QueueItem(TreeNode node, int steps)
{
this.node = node;
this.steps = steps;
}
}
public class Solution
{
public int FindClosestLeaf(TreeNode root, int k)
{
Hashtable nodeParent = new Hashtable();
CreateTreeNodeParent(root, null, nodeParent);
TreeNode target = FindK(root, k);
//BFS
Queue queue = new Queue();
Hashtable visited = new Hashtable();
QueueItem qi = new QueueItem(target, 0);
queue.Enqueue(qi);
visited.Add(target.val, true);
int minDistance = Int32.MaxValue;
int minNodeVal = -1;
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
QueueItem currentQi = queue.Dequeue();
if (currentQi.node != null && currentQi.node.left == null && currentQi.node.right == null)
{
if (currentQi.steps < minDistance)
{
minDistance = currentQi.steps;
minNodeVal = currentQi.node.val;
}
}
//Children:
if (currentQi.node.left != null && !visited.ContainsKey(currentQi.node.left.val))
{
QueueItem leftQueueItem = new QueueItem(currentQi.node.left, currentQi.steps + 1);
queue.Enqueue(leftQueueItem);
visited.Add(currentQi.node.left.val, true);
}
if (currentQi.node.right != null && !visited.ContainsKey(currentQi.node.right.val))
{
QueueItem rightQueueItem = new QueueItem(currentQi.node.right, currentQi.steps + 1);
queue.Enqueue(rightQueueItem);
visited.Add(currentQi.node.right.val, true);
}
//Parent:
TreeNode parent = (TreeNode)nodeParent[currentQi.node.val];
if (parent != null && !visited.ContainsKey(parent.val))
{
QueueItem parentQueueItem = new QueueItem(parent, currentQi.steps + 1);
queue.Enqueue(parentQueueItem);
visited.Add(parent.val, true);
}
}
return minNodeVal;
}
public TreeNode FindK(TreeNode node, int k)
{
if (node != null)
{
if (node.val == k) return node;
TreeNode left = FindK(node.left, k);
if (left != null) return left;
TreeNode right = FindK(node.right, k);
return right;
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
public void CreateTreeNodeParent(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent, Hashtable nodeParent)
{
if (node != null)
{
nodeParent.Add(node.val, parent);
CreateTreeNodeParent(node.left, node, nodeParent);
CreateTreeNodeParent(node.right, node, nodeParent);
}
}
}




Comments
Post a Comment