Deep Copy of Data Structure - A Classic Problem
This is actually a classic problem - how to make a deep copy of a data structure? https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-binary-tree-with-random-pointer/
The tree is represented in the same input/output way as normal binary trees where each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (in the input) where the random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
You will be given the tree in class Node and you should return the cloned tree in class NodeCopy. NodeCopy class is just a clone of Node class with the same attributes and constructors.
Example 1:

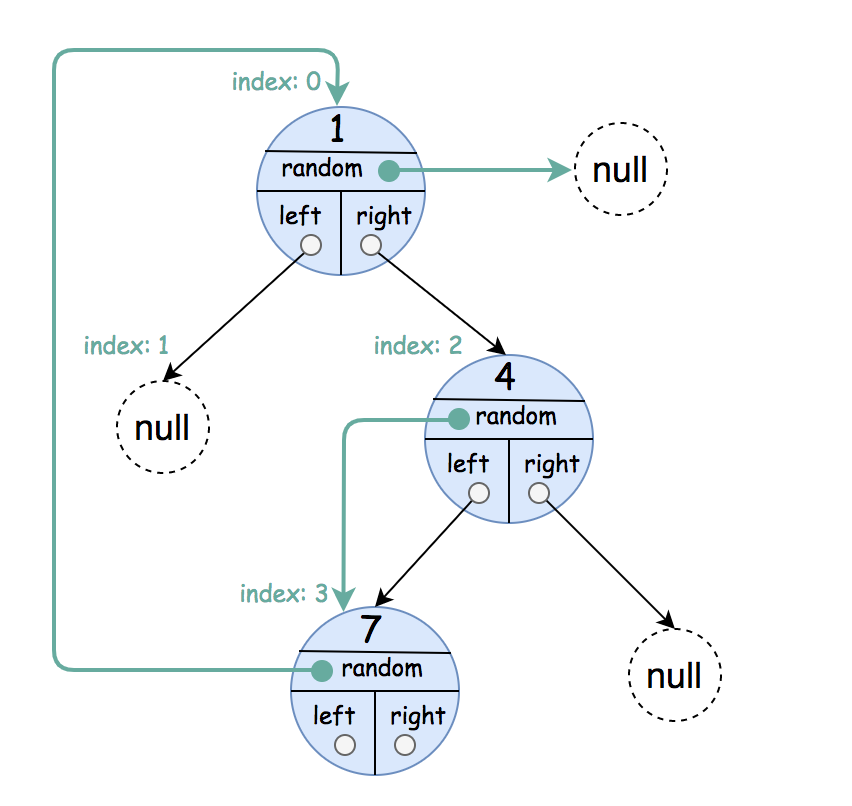
Input: root = [[1,null],null,[4,3],[7,0]] Output: [[1,null],null,[4,3],[7,0]] Explanation: The original binary tree is [1,null,4,7]. The random pointer of node one is null, so it is represented as [1, null]. The random pointer of node 4 is node 7, so it is represented as [4, 3] where 3 is the index of node 7 in the array representing the tree. The random pointer of node 7 is node 1, so it is represented as [7, 0] where 0 is the index of node 1 in the array representing the tree.
Example 2:

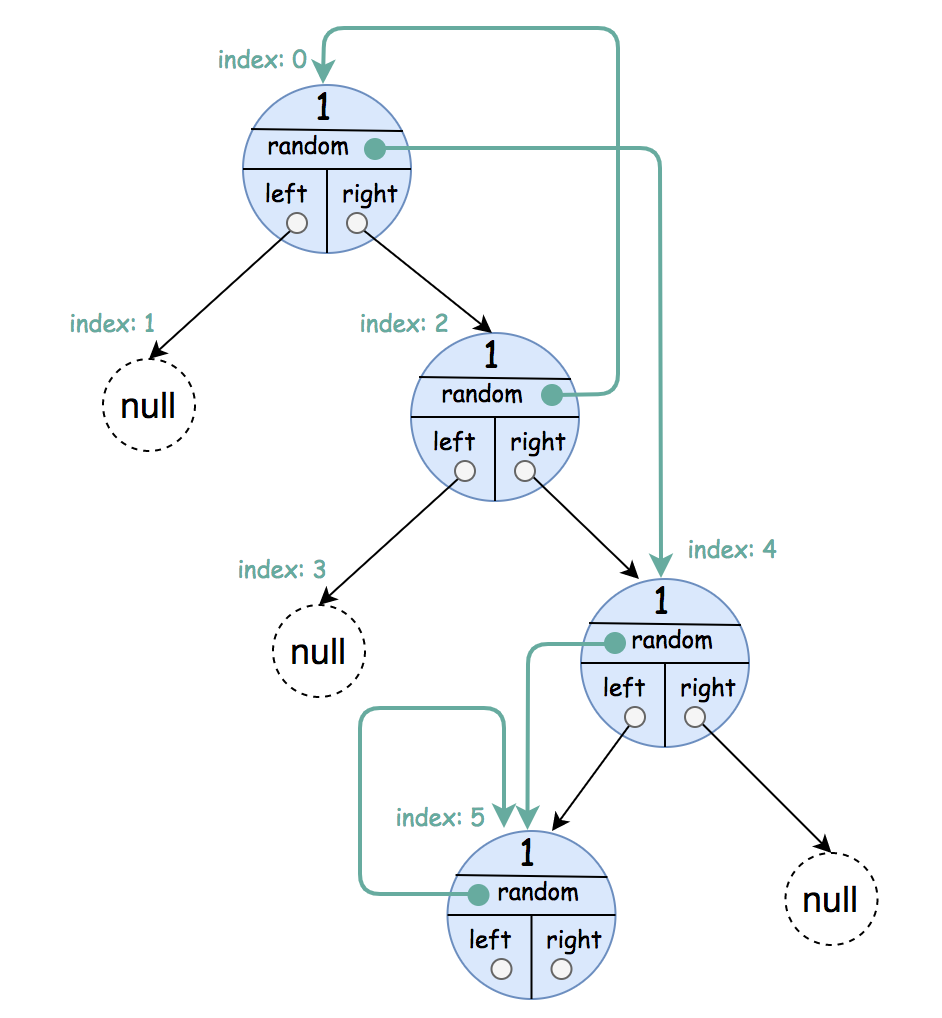
Input: root = [[1,4],null,[1,0],null,[1,5],[1,5]] Output: [[1,4],null,[1,0],null,[1,5],[1,5]] Explanation: The random pointer of a node can be the node itself.
Example 3:

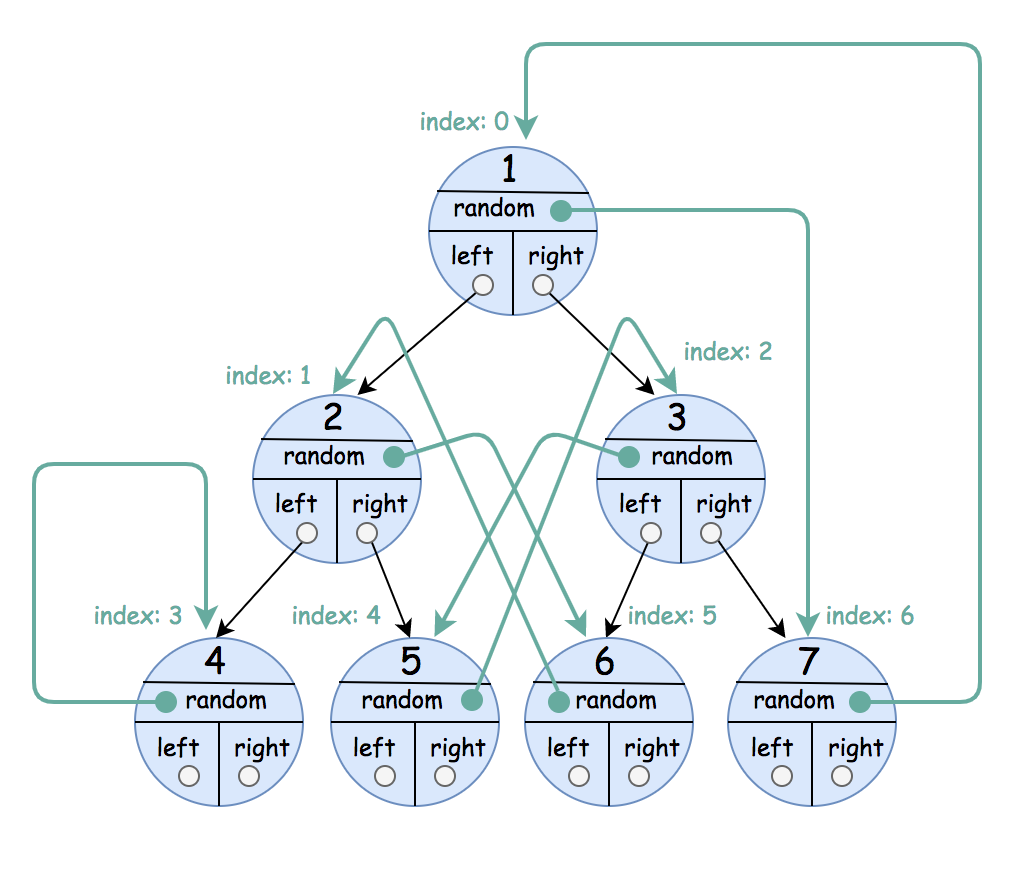
Input: root = [[1,6],[2,5],[3,4],[4,3],[5,2],[6,1],[7,0]] Output: [[1,6],[2,5],[3,4],[4,3],[5,2],[6,1],[7,0]]
Example 4:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 5:
Input: root = [[1,null],null,[2,null],null,[1,null]] Output: [[1,null],null,[2,null],null,[1,null]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the
treeis in the range[0, 1000]. - Each node's value is between
[1, 10^6].
One technique that I find really valuable for this problem is to split it into two parts, and make use of a hash map. Here is the gist of it:
a) As mentioned, have a Hash Map handy
b) Perform a Shallow Copy first. A shallow copy means that you'll make a copy of the initial data structure without worrying about the random pointer. However, as you make a copy, create a map in the hash map between a node in the source data structure to the corresponding node in the target data structure. This can be done with a DFS.
c) Finally, perform a Deep Copy. The deep copy consists of a pre-order DFS using the hash map to map the random pointer.
For the cost, it costs O(2N)-time for {b,c} and O(N)-space for (a). Code is below, and since it is my Birthday today, comes with a pic of me :) Cheers, ACC.
public class Solution
{
public NodeCopy CopyRandomBinaryTree(Node root)
{
if (root == null) return null;
NodeCopy target = new NodeCopy(root.val);
Hashtable sourceToTarget = new Hashtable();
sourceToTarget.Add(root.GetHashCode(), target);
//Step 1: Shallow copy with hash map
ShallowCopy(root, target, sourceToTarget);
//Step 2: deep copy of random node using hash map
DeepCopy(root, target, sourceToTarget);
return target;
}
private void DeepCopy(Node source,
NodeCopy target,
Hashtable sourceToTarget)
{
if (source == null) return;
if (source.random != null && sourceToTarget.ContainsKey(source.random.GetHashCode()))
{
target.random = (NodeCopy)sourceToTarget[source.random.GetHashCode()];
}
DeepCopy(source.left, target.left, sourceToTarget);
DeepCopy(source.right, target.right, sourceToTarget);
}
private void ShallowCopy(Node source,
NodeCopy target,
Hashtable sourceToTarget)
{
if (source == null) return;
if (source.left != null)
{
target.left = new NodeCopy(source.left.val);
if (!sourceToTarget.ContainsKey(source.left.GetHashCode())) sourceToTarget.Add(source.left.GetHashCode(), target.left);
ShallowCopy(source.left, target.left, sourceToTarget);
}
if (source.right != null)
{
target.right = new NodeCopy(source.right.val);
if (!sourceToTarget.ContainsKey(source.right.GetHashCode())) sourceToTarget.Add(source.right.GetHashCode(), target.right);
ShallowCopy(source.right, target.right, sourceToTarget);
}
}
}





Comments
Post a Comment