Prefix Sum: Trading Space for Time
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Example 1:
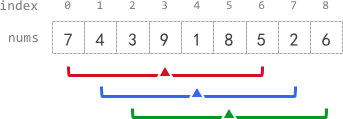
Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: - avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index. - The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37. Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5. - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4. - For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4. - avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 Output: [100000] Explanation: - The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000. avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 Output: [-1] Explanation: - avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
public int[] GetAverages(int[] nums, int k)
{
long[] prefixSum = new long[nums.Length];
prefixSum[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
prefixSum[i] = nums[i] + prefixSum[i - 1];
}
int[] retVal = new int[nums.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < retVal.Length; i++)
{
if (i - k >= 0 && i + k < retVal.Length)
{
retVal[i] = (int)((prefixSum[i + k] - prefixSum[i - k] + nums[i - k]) / (2 * k + 1));
}
else
{
retVal[i] = -1;
}
}
return retVal;
}




Comments
Post a Comment