Hints in the problem description can really simplify your solution
Take a look at this particular problem (medium). If you read it carefully, the solution might be easier than an "easy" problem:
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-a-corresponding-node-of-a-binary-tree-in-a-clone-of-that-tree/
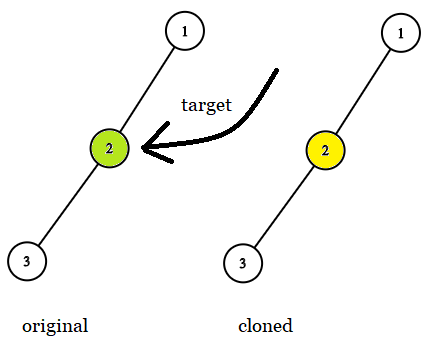
The key point, after you read the question, is this one:
The values of the nodes of the tree are unique
Well, that being said, and given that you have a pointer to the node in the original tree, you instantly have the value that you're looking for. Hence, the whole problem reduces to the following problem:
public class Solution
{
public TreeNode GetTargetCopy(TreeNode original, TreeNode cloned, TreeNode target)
{
return FindNode(cloned, target.val);
}
private TreeNode FindNode(TreeNode node, int target)
{
if (node == null) return null;
if (node.val == target) return node;
TreeNode left = FindNode(node.left, target);
if (left != null) return left;
TreeNode right = FindNode(node.right, target);
return right;
}
}
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-a-corresponding-node-of-a-binary-tree-in-a-clone-of-that-tree/
1379. Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
Medium
Given two binary trees
original and cloned and given a reference to a node target in the original tree.
The
cloned tree is a copy of the original tree.
Return a reference to the same node in the
cloned tree.
Note that you are not allowed to change any of the two trees or the
target node and the answer must be a reference to a node in the cloned tree.
Follow up: Solve the problem if repeated values on the tree are allowed.
Example 1:

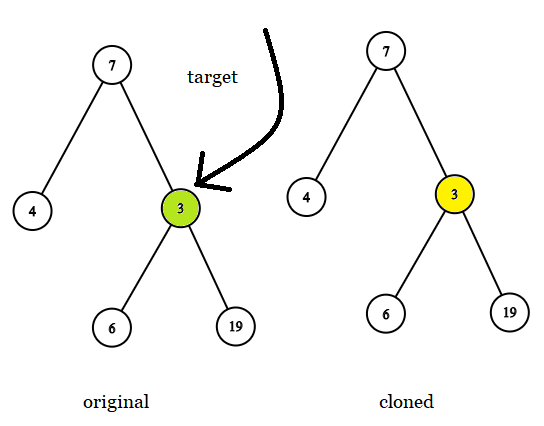
Input: tree = [7,4,3,null,null,6,19], target = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: In all examples the original and cloned trees are shown. The target node is a green node from the original tree. The answer is the yellow node from the cloned tree.
Example 2:

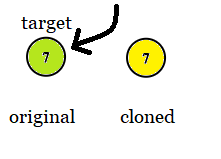
Input: tree = [7], target = 7 Output: 7
Example 3:

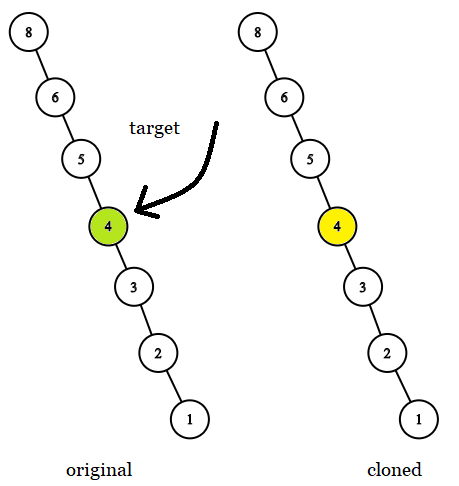
Input: tree = [8,null,6,null,5,null,4,null,3,null,2,null,1], target = 4 Output: 4
Example 4:

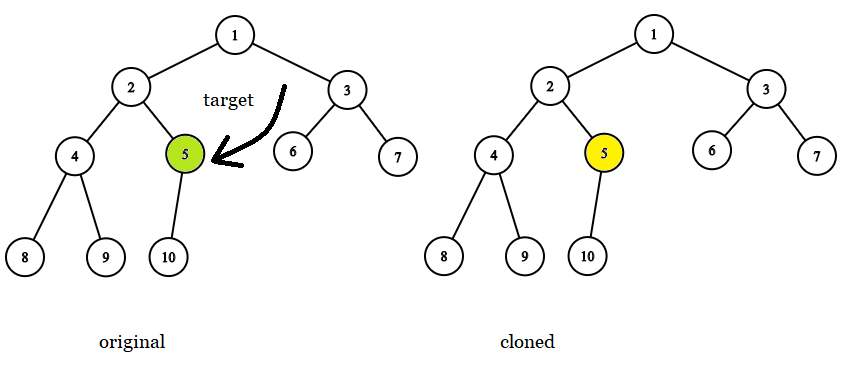
Input: tree = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], target = 5 Output: 5
Example 5:

Input: tree = [1,2,null,3], target = 2 Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the
treeis in the range[1, 10^4]. - The values of the nodes of the
treeare unique. targetnode is a node from theoriginaltree and is notnull.
Accepted
398
Submissions
469
The key point, after you read the question, is this one:
The values of the nodes of the tree are unique
Well, that being said, and given that you have a pointer to the node in the original tree, you instantly have the value that you're looking for. Hence, the whole problem reduces to the following problem:
Given a tree with unique values and a value N, return the tree node whose value is NAnd this is a problem that can easily be solved in O(n)-time, O(1)-space. Code is below, cheers, ACC.
public class Solution
{
public TreeNode GetTargetCopy(TreeNode original, TreeNode cloned, TreeNode target)
{
return FindNode(cloned, target.val);
}
private TreeNode FindNode(TreeNode node, int target)
{
if (node == null) return null;
if (node.val == target) return node;
TreeNode left = FindNode(node.left, target);
if (left != null) return left;
TreeNode right = FindNode(node.right, target);
return right;
}
}



Comments
Post a Comment