Simple Traversals in Binary Trees II
This one requires a standard pre-order, keeping track of the concatenated strings, until we reach the kth element, in which case it is safe to save the result, and return. Code is down below, cheers, ACC.
Extract Kth Character From The Rope Tree - LeetCode
You are given the root of a binary tree and an integer k. Besides the left and right children, every node of this tree has two other properties, a string node.val containing only lowercase English letters (possibly empty) and a non-negative integer node.len. There are two types of nodes in this tree:
- Leaf: These nodes have no children,
node.len = 0, andnode.valis some non-empty string. - Internal: These nodes have at least one child (also at most two children),
node.len > 0, andnode.valis an empty string.
The tree described above is called a Rope binary tree. Now we define S[node] recursively as follows:
- If
nodeis some leaf node,S[node] = node.val, - Otherwise if
nodeis some internal node,S[node] = concat(S[node.left], S[node.right]).
Return k-th character of the string S[root].
Note: If s and p are two strings, concat(s, p) is a string obtained by concatenating p to s. For example, concat("ab", "zz") = "abzz".
Example 1:
Input: root = [10,4,"abcpoe","g","rta"], k = 6 Output: "b" Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val. You can see that S[root] = concat(concat("g", "rta"), "abcpoe") = "grtaabcpoe". So S[root][5], which represents 6th character of it, is equal to "b".
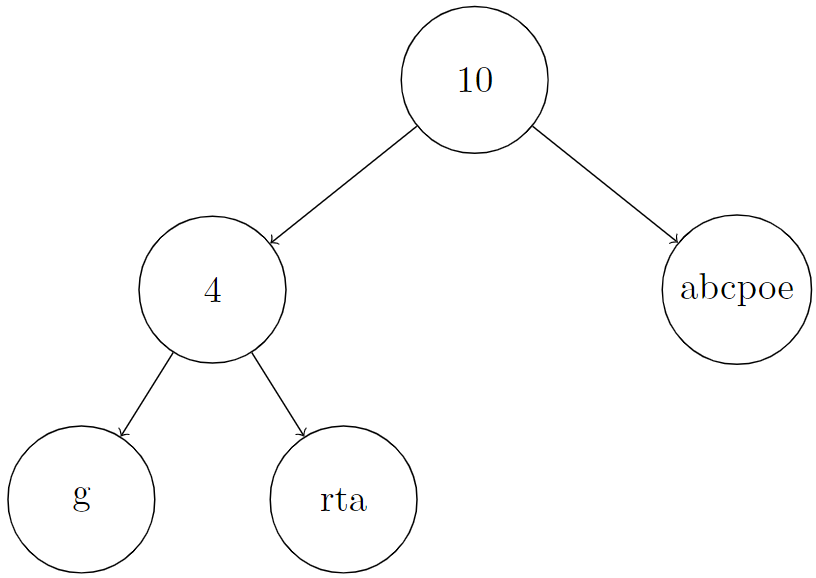
Example 2:
Input: root = [12,6,6,"abc","efg","hij","klm"], k = 3 Output: "c" Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val. You can see that S[root] = concat(concat("abc", "efg"), concat("hij", "klm")) = "abcefghijklm". So S[root][2], which represents the 3rd character of it, is equal to "c".
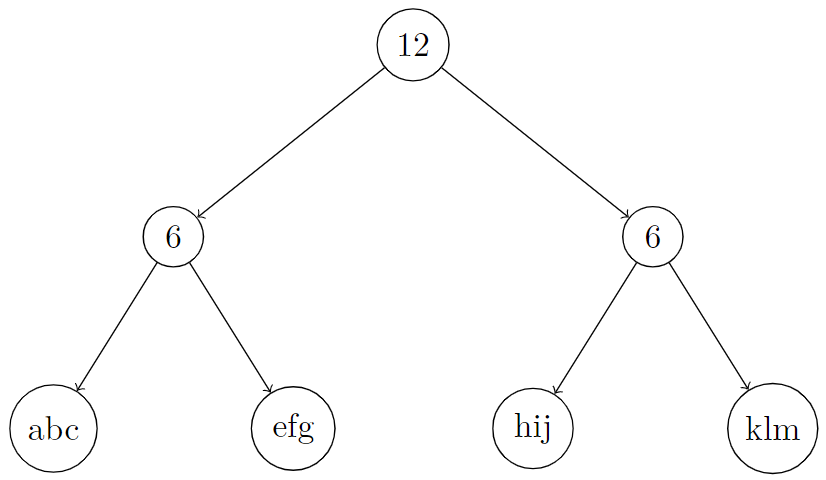
Example 3:
Input: root = ["ropetree"], k = 8 Output: "e" Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val. You can see that S[root] = "ropetree". So S[root][7], which represents 8th character of it, is equal to "e".
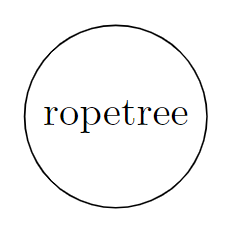
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 103] node.valcontains only lowercase English letters0 <= node.val.length <= 500 <= node.len <= 104- for leaf nodes,
node.len = 0andnode.valis non-empty - for internal nodes,
node.len > 0andnode.valis empty 1 <= k <= S[root].length
public char GetKthCharacter(RopeTreeNode root, int k)
{
char retVal = ' ';
string str = "";
GetKthCharacter(root, ref str, k, ref retVal);
return retVal;
}
private bool GetKthCharacter(RopeTreeNode node,
ref string str,
int k,
ref char retVal)
{
if (node == null) return false;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
str += node.val;
if (str.Length >= k)
{
retVal = str[k - 1];
return true;
}
}
return GetKthCharacter(node.left, ref str, k, ref retVal) || GetKthCharacter(node.right, ref str, k, ref retVal);
}




Comments
Post a Comment